After Loki gets away with the crazy-powerful tesseract and a handful of S.H.I.E.L.D. (seriously that’s a pain to type) agents, Fury has a virtual meeting with members of the World Security Council—which is shadowy in appearance and details. To conduct this furtive conference Fury walks into a room custom-built for such purposes.
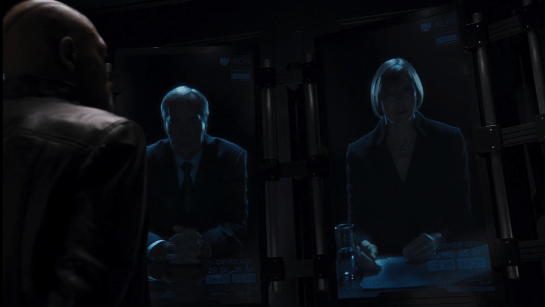
A bank of large vertically-mounted monitors forms a semicircle in the small room, each mounted above a workstation with keyboard and multiple screens overlit for maximum eyestrain. It’s quite unclear what the agents who normally work here are currently doing, or what those vertically mounted screens normally display, since they’d be a shoo-in for an OSHA lawsuit, given the amount a user would need to crane. Ergonomics, Nick, look it up.
Each screen dedicates most of its real estate to a waist-up view of the speaker. Overlays near the bottom assure us that DATA [is] SECURE and confirms it with a 16-character alphanumeric CYPHER KEY that is frequently changing and unique to each speaker. This is similar to an HMAC-based One-time Password Algorithm (HOTP) password algorithm, so is well-grounded in reality. It’s convincing.
The screens adhere to the trope that every screen is a camera. Nick looks at their eyes and they look right back. Ordinarily that would be a big problem, but with the translucent displays and the edge lighting of the participants, it could actually work.
There is no indication of controls for these screens, but that’s cool if the room is dedicated to this purpose. Someone else would set the call up for him, and all he has to do is walk in. He should be able to just walk out to end it. And let them know how he feels about them.